Building an AI-Ready Infrastructure
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the hottest topic in technology for many reasons, good and bad, but it’s happening and it’s here to stay, so how do we build the infrastructure necessary to support it?
To start with, we should recognise that there are many forms of AI. The one that has created the most buzz is generative AI, as seen in ChatGPT, Meta's LLaMA, Claude, Google’s Gemini, and others. Generative AI relies on LLMs (Large Language Models) which have to be trained using vast amounts of data. These LLMs sit in data centres around the world, interconnected by vast fibre networks.
The data centre industry has not stopped talking about AI for at least 18 months, as it gears up for an ‘explosion’ in demand for new capacity. Some of the most respected voices in technology have predicted immense amounts of growth in data centre requirements, with predictions of triple the current capacity within 10 years being at the conservative end. That’s three times the current global data centre market, which has taken 30 years or more to get to where it is today. And, when we say growth, we’re talking about power. AI systems will require three times more electricity than data centres currently consume. Depending on who you ask, that’s about 2-4% of today’s global electricity production. And we’re talking about tripling that, or more.
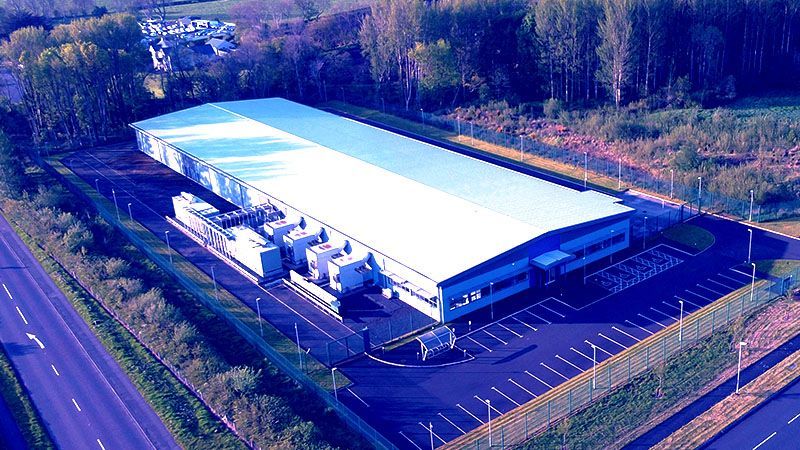
Data Centres
So, what is ‘AI-ready infrastructure’ and how are we going to build it? The two key elements are data centres (to house the AI systems) and networks (to connect them with the rest of the world). LLM training typically uses servers with GPUs (the chip of choice for AI) and, for various technical reasons, these work best when in close physical proximity to each other – in other words, GPUs work best in large numbers in large data centres. Not just that, but the new generations of GPUs work best in dense data centres, meaning that each rack or cabinet of AI kit needs a lot of power.
Most data centres are designed to accommodate older kit that is not so power hungry. The average consumption globally is about 8kW per rack, although many still operate at about 2kW per rack. The latest nVidia (the leading GPU manufacturer) array needs a colossal 120kW per rack. The infrastructure inside a data centre designed for these beasts is complex: the cooling systems (GPUs run very hot) and electrical distribution systems are much harder to design and set up, and are also expensive.
So, data centres for AI training systems are mostly going to be new, as adapting older facilities is a non-starter. So, where do you put them? Finding land next to the vast amounts of electricity required is increasingly difficult in many European countries, especially in the UK. Most of the utility grids in Europe are severely lacking in spare capacity, and building new grid connections and electricity generation is a slow and expensive process.
The answer might be to locate these new AI data centres near new renewable energy generation sites, but those are few and far between, so land with access to power now carries a hefty premium. Small nuclear reactors could also be an answer but might take a few years to materialise – we know how to build them (witness the nuclear submarine industry) but getting planning permission to put them on land is another matter.
All in all, the data centre industry seems to be at least a few years away from being able to provide the massive upgrade in capacity that is expected. Even solving the land/power problem leaves the issue of actually building a new scale of data centre, 10 or 20 times bigger than what most would consider to be a gigantic site today. It can be done, we can solve the engineering challenges, but these are huge construction projects.
Networks
What about the networks? Actually, although very little real research has been done on the impact of large-scale AI rollouts on existing networks, we might be in a better position. The fibre networks in the UK and many European countries have benefited from significant investment over the last few years, so coverage is a lot better than it used to be. That does not mean that fast and large fibre routes, which will be a necessity for most AI systems, are all there, but it will be easier to build out new capacity than it will be to find power. Still, what we really need is some serious research into the amount of data that will need to be moved about and how that maps with existing network infrastructure.
All in all, we have more questions than answers. Some people in the infrastructure industry are sceptical that things will ever get to the scale that some are predicting, but most of us do expect it to happen – it’s just a matter of time, and the race has already begun.
Cambridge Management Consulting
Duncan Clubb is a Senior Partner at Cambridge Management Consulting, specialising in data centre and edge compute strategy. Duncan has extensive experience as an IT consultant and practitioner and has worked with many leading organisations in the financial, oil and gas, retail, and healthcare sectors. He is widely regarded as a leading expert and is a regular speaker at industry events.
If you or your organisation require support preparing your Digital Infrastructure for the emerging AI-industry, you can read about our array of Data Centre services, and get in touch with Duncan Clubb, through our designated
Telecoms, Media, and Technology service page.
Contact - NIS2 Article
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Blog Subscribe
SHARE CONTENT