The Time is Now for African Investment
Africa has a young population and is growing fast
Establishing and supporting businesses in Africa is twinned with risk; but this is not an uncommon partnership. High-risk endeavours usually have the highest rewards. African investment also includes the opportunity to have a positive impact on local and national infrastructure, SDGs, the economy, and the digital divide.
Africa is made up of 54 countries, according to the United Nations (UN). It is larger than the United States, China, India, Japan and the whole of Europe put together.
Most of these countries are underdeveloped, with poor infrastructure and degrees of governmental instability. It has been reported that Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) was the world’s slowest growing region in 2021. SSA also has some of the most expensive 1GB basket prices globally.
There is a clear international focus on Africa. The second largest continent is receiving significant investment which is financing the roll-out of data centres, fibre connectivity in new areas, and the deployment of mobile networks in key markets.
Africa is home to 1.4 billion people, accounting for 16.72% of the world’s population. This is predicted to rise to 4.39 billion by 2100.
It is the most central continent in the world, making Africa the perfect hub for reaching the four corners of the world. It is also the most profitable region in the world. According to the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC), Africa offers the highest returns on foreign direct investment (FDI) globally. In fact, according to the recent UN Conference on Trade and Development, Africa’s return on foreign investment between 2006 to 2011 reached 11.4%— significantly more than the global average of 7.1%.
Currently, the top three recipient countries in Africa for FDI in 2020 were Egypt, The Republic of the Congo and South Africa. Since 1 January 2021, the African Continental Free Trade Area has been in effect, creating the world’s largest free-trade area with all 54 countries participating. This agreement essentially creates one single market allowing foreign businesses to reach markets that were once difficult to approach.
The median age across Africa is 19.7 years.
Africa has a young and growing workforce: a perfect condition for businesses wanting to invest. Africa is the fastest growing continent, and by the turn of the century will be the only region with population growth.
Six of the world’s 12 fastest-growing countries are in Africa (Ethiopia, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Mozambique, Tanzania and Rwanda).
With almost 60% of the population under 25 years old, it is also the youngest continent. There is a surplus of workers that want and need jobs. Unlike other parts of the world, Africa is not in a candidate-driven market; it’s an employer market and that means your business can recruit the best talent, without facing fierce competition. A young and abundant labour market also has the advantage of lowering production costs. Foreign investment will hopefully have the additional advantage of raising wage rates in Africa and improving market efficiency.
Africa is the least-developed continent, barring Antarctica. With its fast-growing population, governments want and need infrastructure projects to support this budding populace. The opportunity for development is huge, and African countries are adopting various measures to attract investors.
Top five growing markets for foreign investment
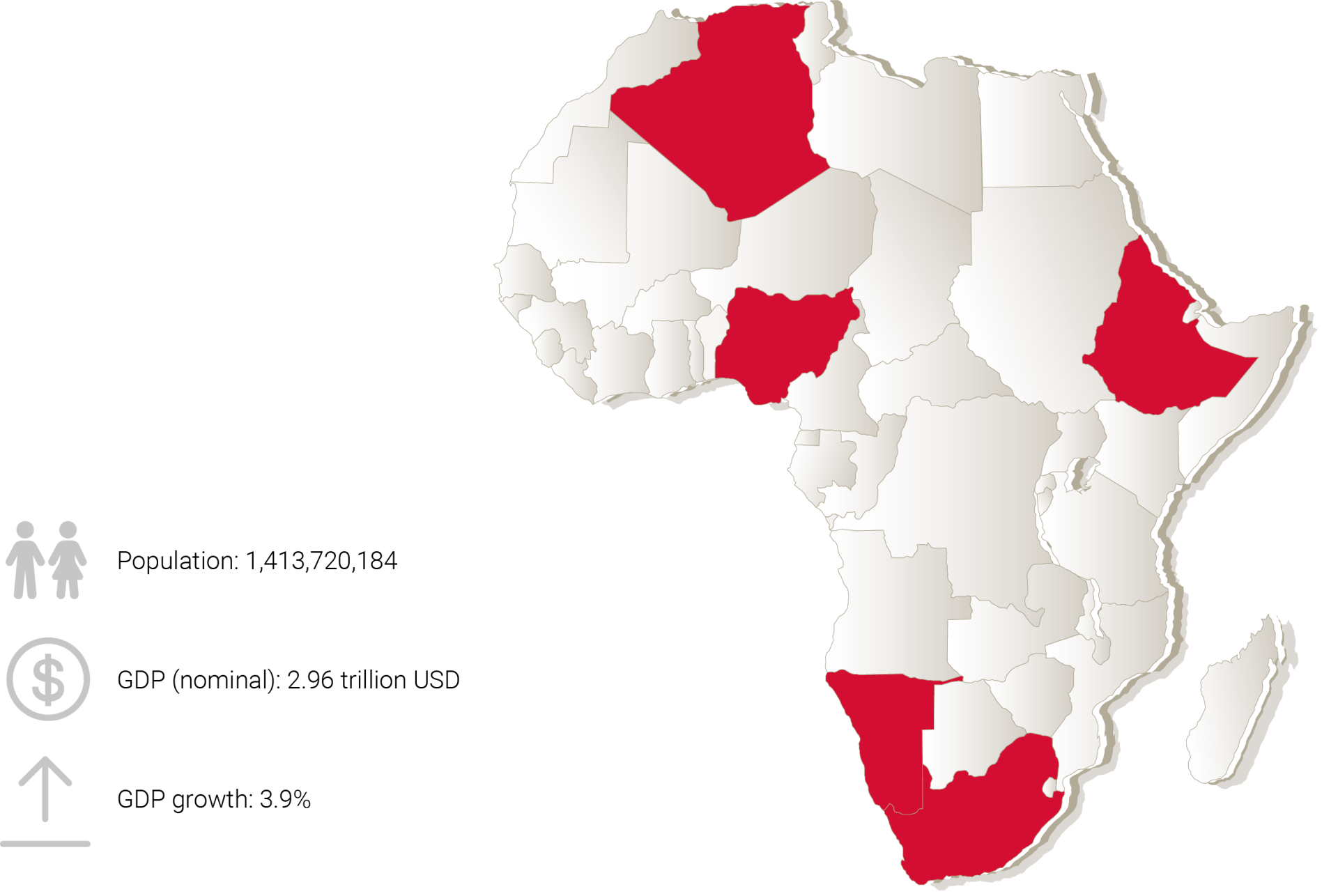
We will take a look at five of the most important emerging markets in Africa: Nigeria, South Africa, Algeria, Ethiopia and Namibia. We make the business case for investment and also assess the matrix of opportunity versus risk.
Nigeria
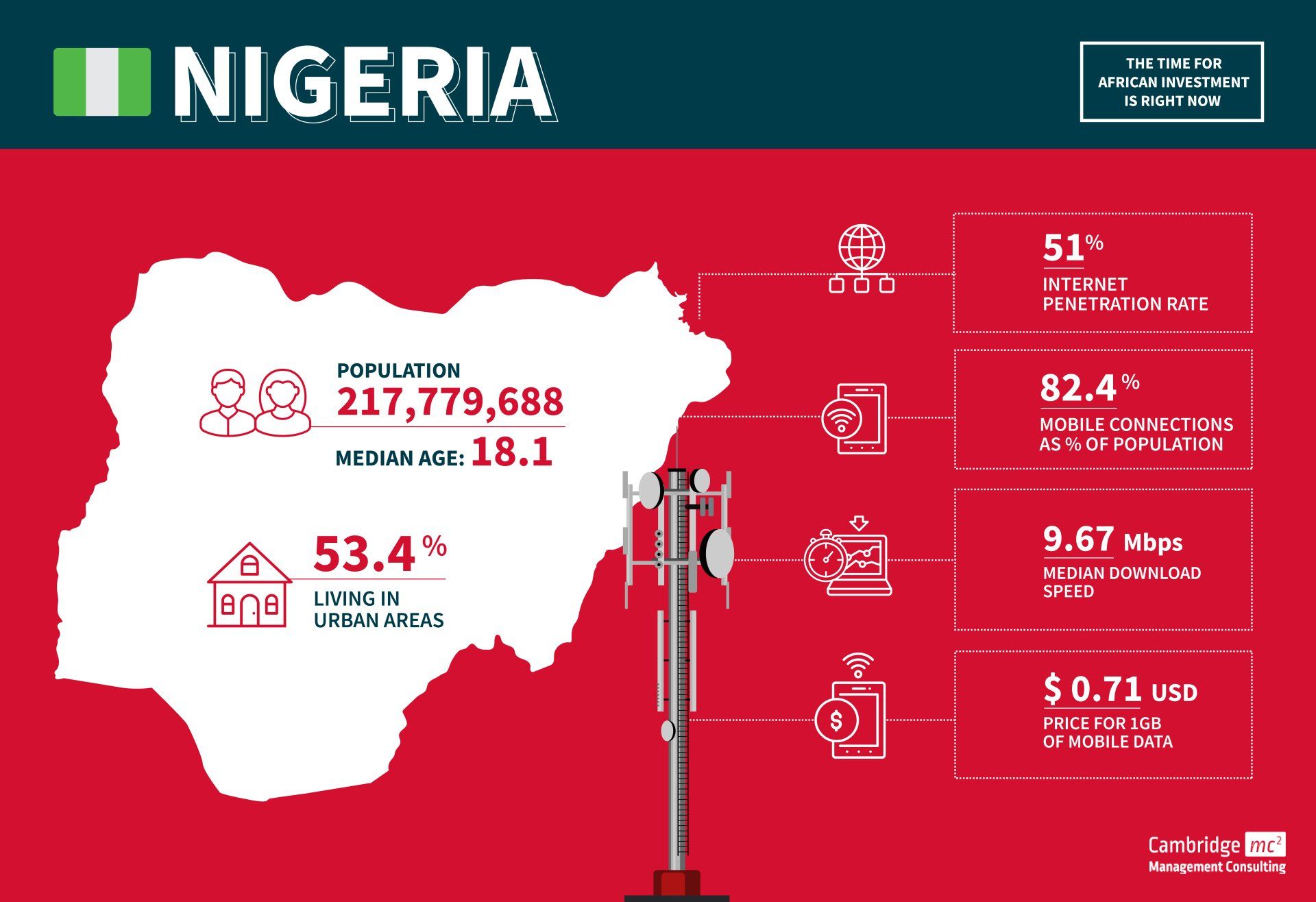
Overview
- Nigeria is the largest market in Africa
- The main language is English
- The population is forecast to grow to over 410 million by 2050
- The legal system is based on the UK system
- One of Africa’s key oil producers, although currently held back by low production. The economy is heavily dependant on this sector and part of the current economic strategy is diversification
- The country is facing severe challenges such as rising inflation, high unemployment and widespread insecurity
MNOs
- MTN
- Glo
- Airtel
Opportunities
- There is a major drive to transform the energy and agricultural sectors through technology
- Key driver of international trade across all of West Africa
- The third largest movie industry after Hollywood and Bollywood
- Deployment of 5G technology and the Federal Government of Nigeria’s broadband penetration target of 70% by 2025 will attract additional foreign investment
- Nigeria plays an important leadership role in both West Africa and on the African continent. The headquarters of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is in Abuja
Challenges
- Although the economy is predicted to grow around 3.2% in the next few years, this projection is subject to significant risks such as further declines in oil production and heightened insecurity
- Unfavourable regulatory changes are continuing to have negative effects on business
- Nigeria ranks 131 on the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business 2020 report — although this is improving year-on-year
- Unreliable power supply
- Poor transportation infrastructure
- Slow judicial system
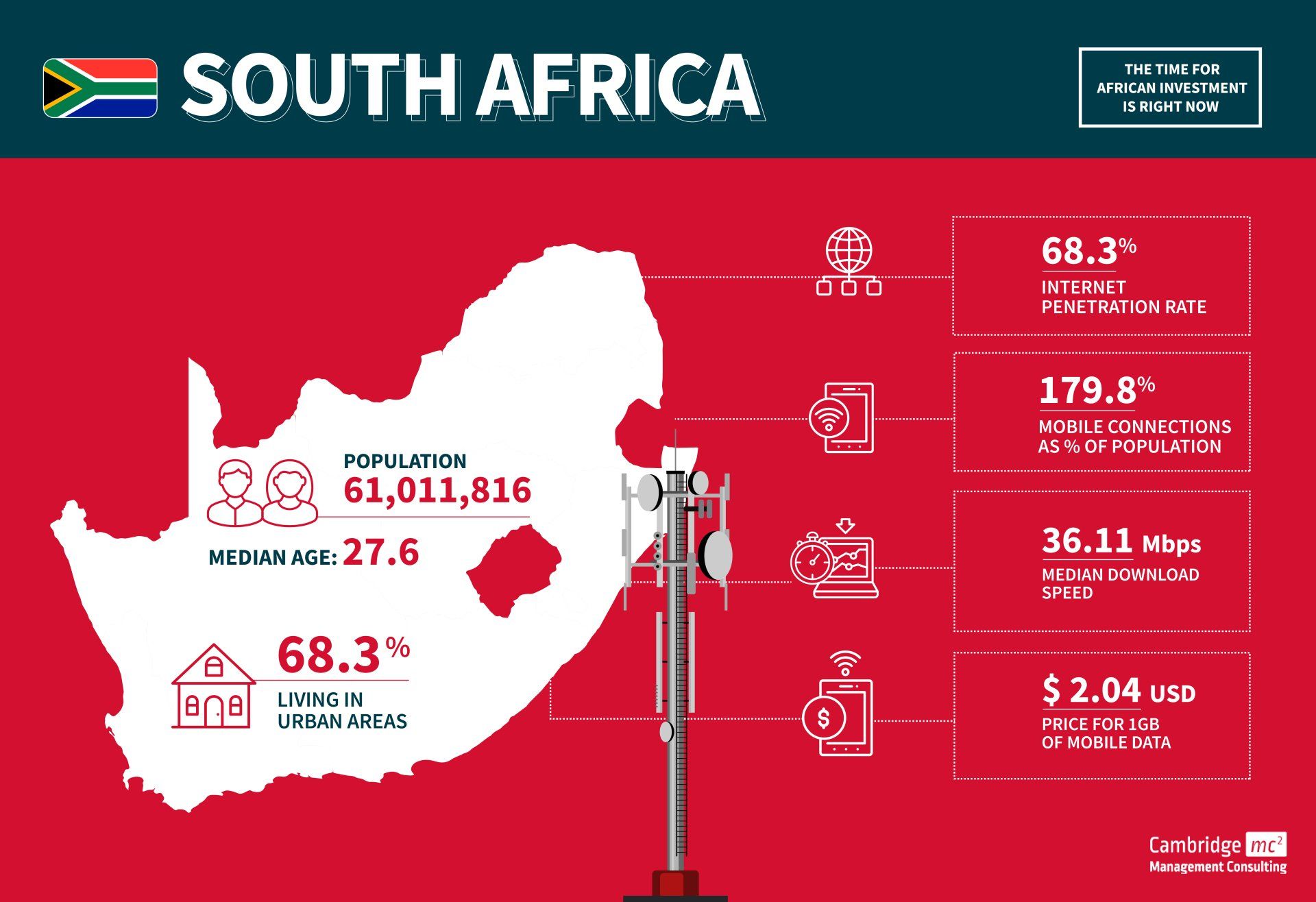
South Africa
Overview
- South Africa is, in general, the most advanced, diversified and productive economy in Africa
- The country was hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic. Poverty has reached levels not seen for more than a decade, while inflation has increased to a 13-year high
- Telecoms growth has decreased despite the boost in traffic during the pandemic. Future growth is expected to be driven by mobile and fixed-broadband digital services
- South Africa is a business incubator for new-to-market ideas which then travel to other Sub-Saharan African markets
- There is widespread use of English for business
- SA has a robust legal sector
MNOs
- MTN
- Cell C
- Vodacom
- Telkom
Opportunities
- Since 2015, over one-third of acquisitions in the African tech space have involved South African companies
- Significant CAPEX investment in new infrastructure required to evolve telco’s business models to compete with new market entrants
- According to the Global Connectivity Index, South Africa is one of the countries with the most potential in using ICT to boost growth and achieve several of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Challenges
- Infrastructure issues continue to hold back the economy and lead to frequent power shortages
- The telecoms market has suffered from reduced profit margins over the last decade. Value-added services and new technologies will be required to realise new revenue streams
- The high cost of connectivity and mobile devices, particularly in the current recession and high unemployment, are a barrier to the uptake of new digital services
- According to the World Bank’s Doing Business project, South Africa’s rank in ease of doing business in 2020 was 84 out of 190
- One of the highest and most persistent inequality rates in the world
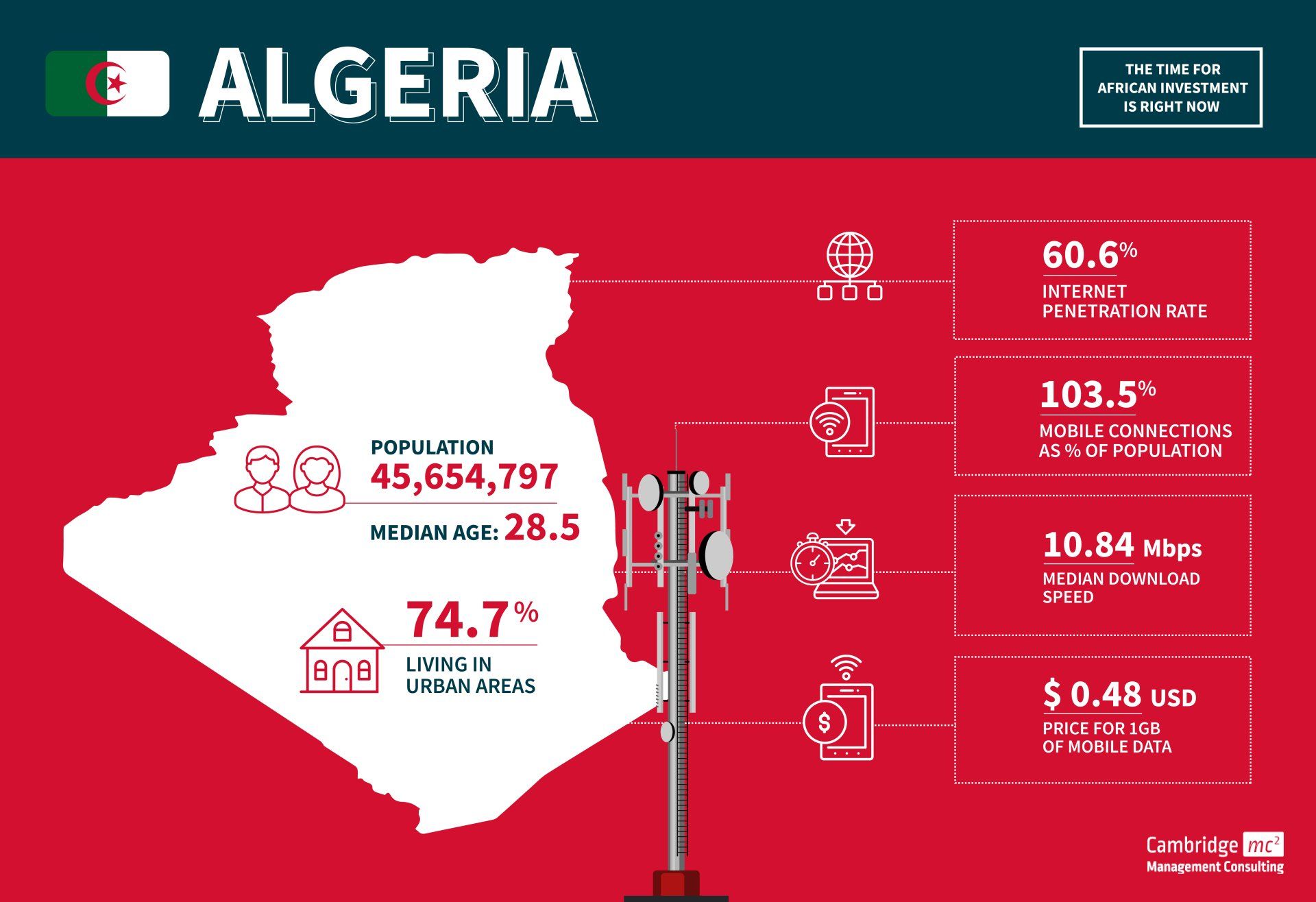
Algeria
Overview
- Algeria is the fourth largest economy in Africa
- Oil and natural gas historically account for 95% of export revenues and 60 percent of total government revenues
- Continuing political instability threatens economic reforms
- The country’s infrastructure primarily relies on 3G and 4G LTE for mobile, and ADSL & fibre for fixed telecommunications
- Algeria connects to Europe via four fibre optic subsea cables
MNOs
- Mobilis
- Djezzy
- Ooredoo Algeria
- Algerie Telecom
Opportunities
- The ICT sector will play a significant role in Algeria’s export diversification strategy as it moves away from oil and gas
- Mobile adoption rates are high, with the number of mobile connections in 2022 equivalent to 103.5% of the total population. Broadband adoption rates are significantly lower at around 9%
- Since 2016, Algeria has deployed more than 120,000 km of optical fibre across the country to help close the gap in broadband adoption rates
Challenges
- Algeria’s state-owned company Algerie Telecom holds a monopoly over the country’s fixed-line and fibre optic networks and it is responsible for developing Algeria’s telecommunication sector
- Algeria ranked 157 out of 190 on the World Bank’s Ease of Doing Business index in 2021
- Corruption in state institutions
- One of the biggest challenges is foreign exchange (Forex) and finance repatriation. It can be very difficult for companies to get their money out
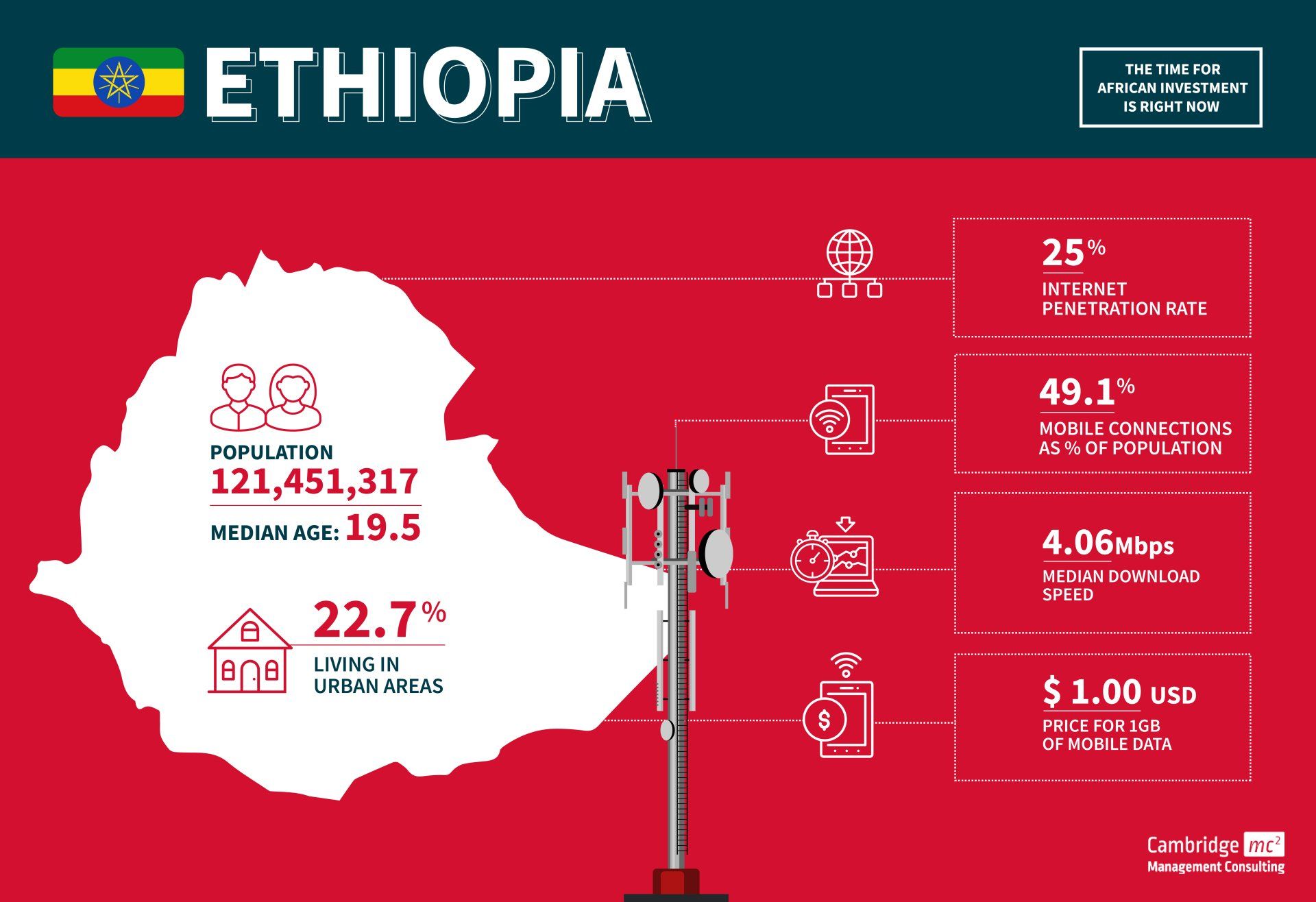
Ethiopia
Overview
- Ethiopia is the second-most populous country in Africa
- It has one of the oldest public telecommunication operators, established in 1894
- Ethiopian telecommunication is one of the least developed in the world. Mobile connections per 100 people is around 49% and internet penetration stands at 25%
- Ethiopia is one of the weakest economies in the world
- As part of its commitment to support Ethiopia’s plan to open up the telecoms sector, the World Bank is preparing a new Digital Ethiopia Foundations project and will invest some $200 million in the country’s digital economy
- The African Union (AU) is headquartered in Addis Ababa
MNOs
- Ethio Telecom
Opportunities
- The Ethiopian government is in the process of privatising state-owned enterprises and has signalled that it will shift toward market-based reforms and more flexibility
- The Government of Ethiopia (GOE) has committed to building a green economy and reaching UN sustainable development goals (SDGs). Ethiopia will mitigate CO2 emissions by expanding electric power generation from renewable sources
- The GOE is open to proposals for energy projects using Independent Power Purchase (IPP) agreements for the sale of power from renewable resources
Challenges
- The economy is still emerging from civil conflict in the north which created substantial social and economic disruption
- The GOE retains control over the utilities sector and prohibits foreign ownership of banking, insurance, and financial services
- State-owned enterprises dominate the economic landscape, reducing room for the private sector to grow and attract foreign investment
- There are frequently energy shortages as demand outpaces supply. New hydropower dams struggle to produce at full capacity. Power transmission lines and distribution facilities are also inadequate
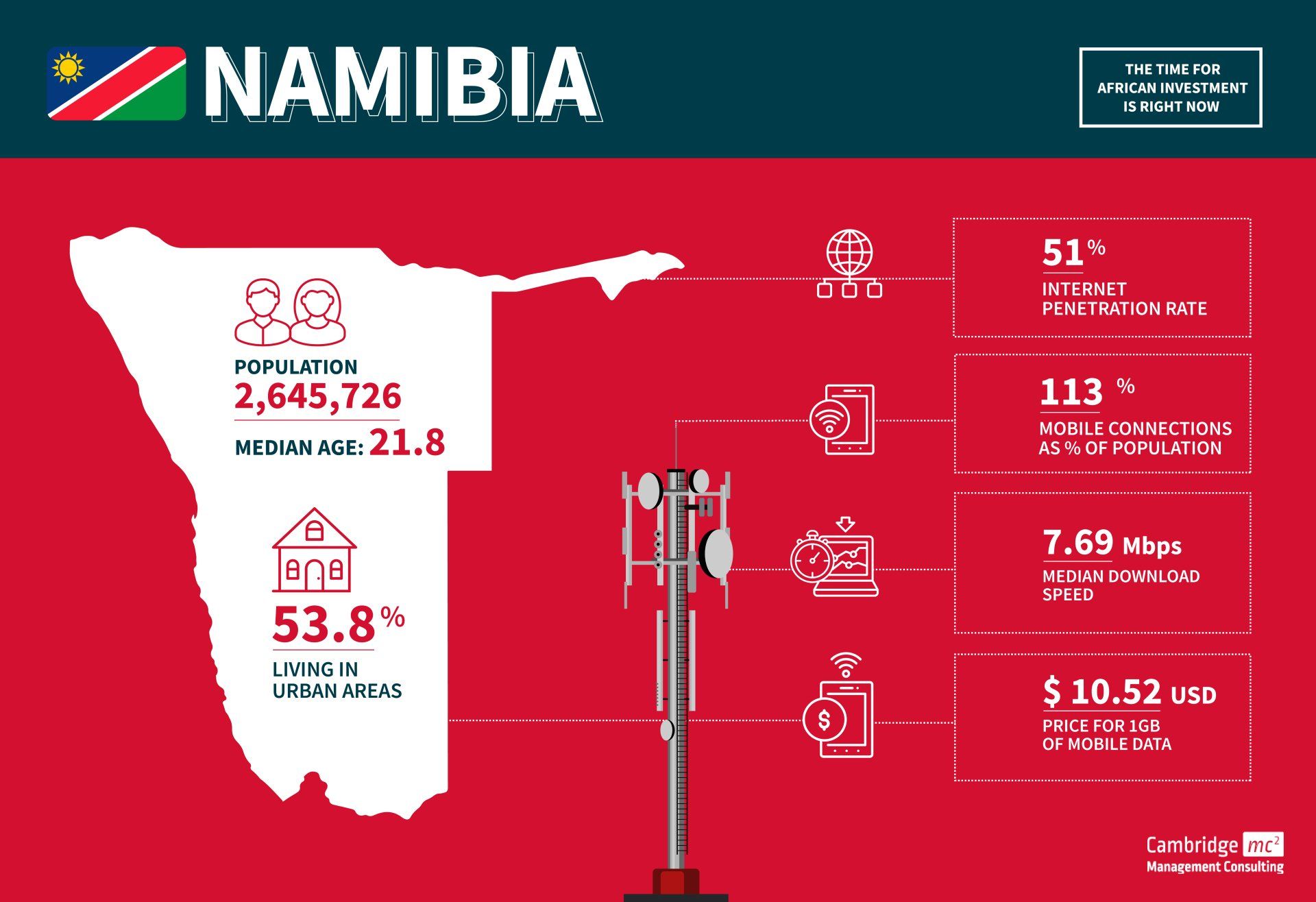
Nambia
Overview
- Namibia is a relatively small market with a population of 2.7 million
- Namibia has one of the most stable political environments in Africa
- Primary infrastructure (roads, rail, air, energy, and telecommunications) is fairly well developed and modern
- The economy is mostly export-driven
- Imports into Namibia are dominated by South Africa, which equate to 45% of Namibia’s total imports
MNOs
- MTC
- TN Mobile (formerly Cell One)
Opportunities
- With the completed expansion of the port at Walvis Bay, Namibia is positioning itself as a gateway to the broader Southern African market and beyond
- The government launched the National Broadband Policy and Implementation Action Plan, which aims to provide universal 2Mb/s services by 2024
- The government is trying to speed up a 5G development strategy after it was initially hampered by public concerns over health implications of the technology—this caused the government to order an environmental assessment of 5G in mid-2020
- Namibia has potential for renewable power investment and plans to build solar, wind, and biomass infrastructure. The government has committed to adding more renewable energy generation sources to its grid
- The government is seeking to attract foreign investors to participate in public-private partnerships (PPPs)
- By the end of 2022, Namibia aims to be connected by a 1,050km branch line of Google’s Equiano cable, running between Portugal and South Africa
Challenges
- High unemployment and critical shortages of skilled labour
- Demand for electricity outstrips domestic supply. Namibia generally escapes any large-scale power outages, but the country remains reliant on buying electricity from South Africa
- Corruption and transparency are often an issue
Opportunities in Africa
If you have an opportunity in Africa, are planning an M&A, or want to partner with an African business we would love to talk to you. At Cambridge Management Consultancy we have a number of consultants who have year's of experience and expertise in the African telecommunications markets. They know how to operate and overcome legal and cultural barriers, as well as having the necessary contacts to help you save time and money. We are excited to share our knowledge and skills to support growth, infrastructure and jobs in these regions. If you want to discuss with one of our team directly then please get in touch with Charles Orsel des Sagets, Steve Brookman, or Andrew Kinnear; or alternatively contact us via the website form below.
Contact - Africa
About Us
Cambridge Management Consulting (Cambridge MC) is an international consulting firm that helps companies of all sizes have a better impact on the world. Founded in Cambridge, UK, initially to help the start-up community, Cambridge MC has grown to over 200 consultants working on projects in 25 countries. Our capabilities focus on supporting the private and public sector with their people, process and digital technology challenges.
What makes Cambridge Management Consulting unique is that it doesn’t employ consultants – only senior executives with real industry or government experience and the skills to advise their clients from a place of true credibility. Our team strives to have a highly positive impact on all the organisations they serve. We are confident there is no business or enterprise that we cannot help transform for the better.
Cambridge Management Consulting has offices or legal entities in Cambridge, London, New York, Paris, Dubai, Singapore and Helsinki, with further expansion planned in future.
Find out more about our
telecommunication services and
full list of capabilities
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Blog Subscribe
SHARE CONTENT